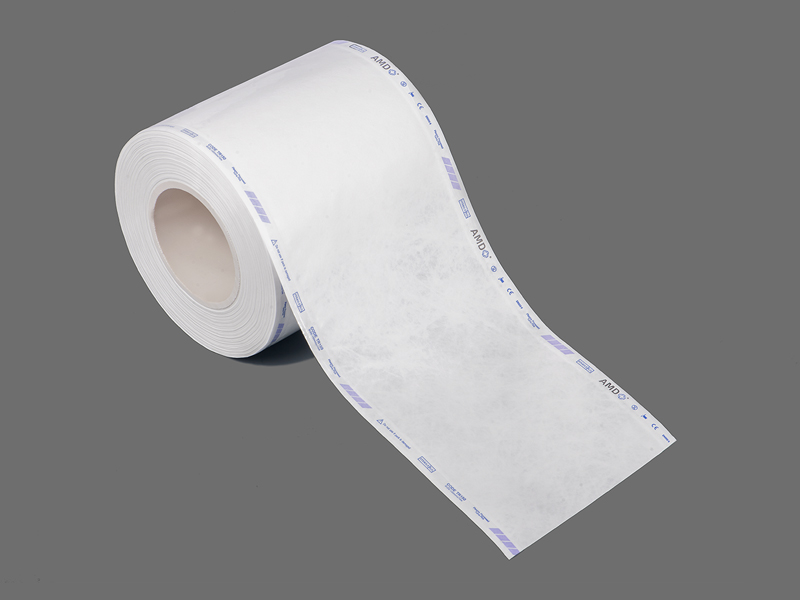
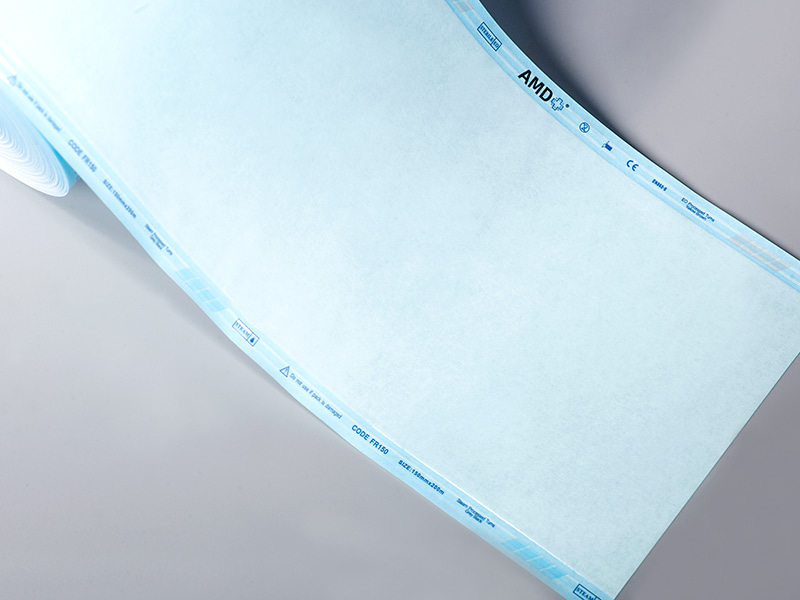
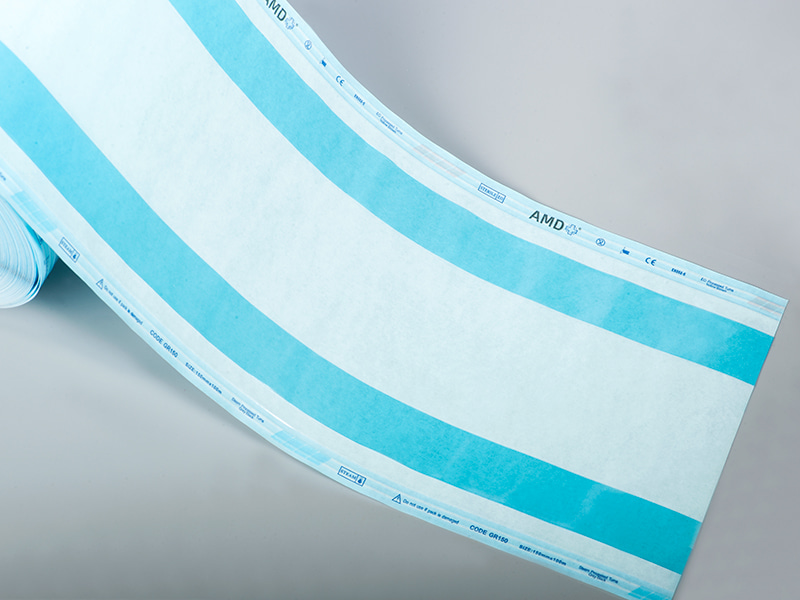
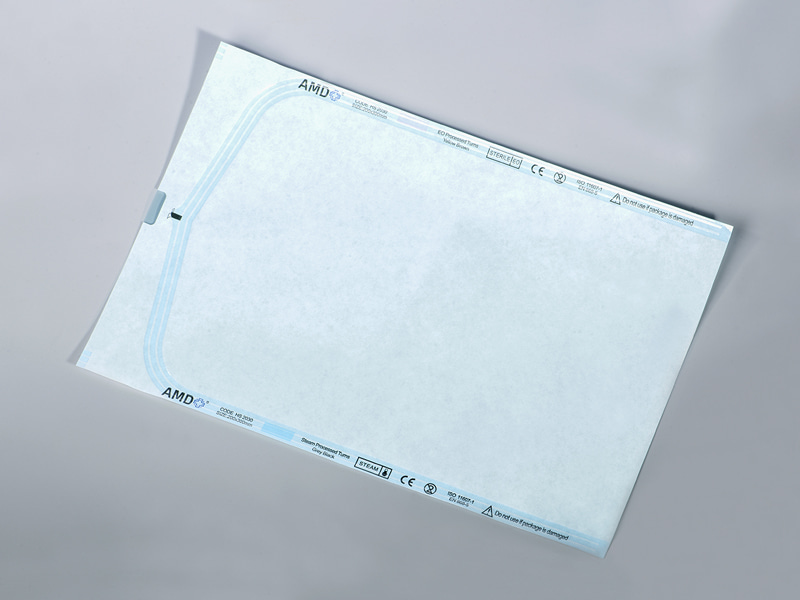
A sterilization self sealing pouch is a single-use package designed for the sterilization and short-term storage of medical instruments and supplies. It combines a porous side that allows the sterilant to reach the contents with a transparent side that makes inspection simple after processing. The “self-sealing” feature is typically an integrated adhesive strip or peel-and-seal closure that removes the need for external heat-sealing equipment during routine packaging tasks. This format has become common in clinics, dental offices and hospital sterile processing areas because it supports fast turnaround while helping to reduce handling errors.
Content
- 1 Why the format matters to sterile processing
- 2 Hopeway AMD and the self sealing pouch market
- 3 Where self sealing pouches fit into standards and regulation
- 4 Common sterilization methods and compatibility
- 5 Practical benefits and operational considerations
- 6 Indicators, labeling and traceability
- 7 Environmental and supply chain themes
- 8 Choosing the right product for your setting
- 9 Industry outlook and closing note
Why the format matters to sterile processing
In health care environments where instruments are reprocessed frequently, packaging must do several jobs at once: permit sterilant penetration, provide a physical barrier to contamination after sterilization, make the contents visible for inventory checks, and allow aseptic presentation at the point of use. Self sealing packages address these needs in a compact, user-friendly form. The built-in closure means staff can seal items quickly and consistently; the clear film lets technicians identify instruments without opening the package; and an integrated chemical indicator on the exterior offers an immediate visual cue that the package has been exposed to a sterilization cycle. These features together streamline workflow while helping teams follow established sterile processing practices.
Hopeway AMD and the self sealing pouch market
Hopeway AMD is among the manufacturers offering self sealing sterilization pouches for clinical and institutional use. The company provides an array of pouch styles that pair medical-grade barrier materials with visible windows and printed indicator areas, intended to support common sterilization methods used across care settings. Hopeway's product information emphasizes compliance with industry quality systems and the importance of matching pouch selection to the sterilant and instrument types in use. This kind of product positioning reflects a wider trend among suppliers to offer solutions that simplify packaging steps while aligning with sterile processing requirements.
Where self sealing pouches fit into standards and regulation
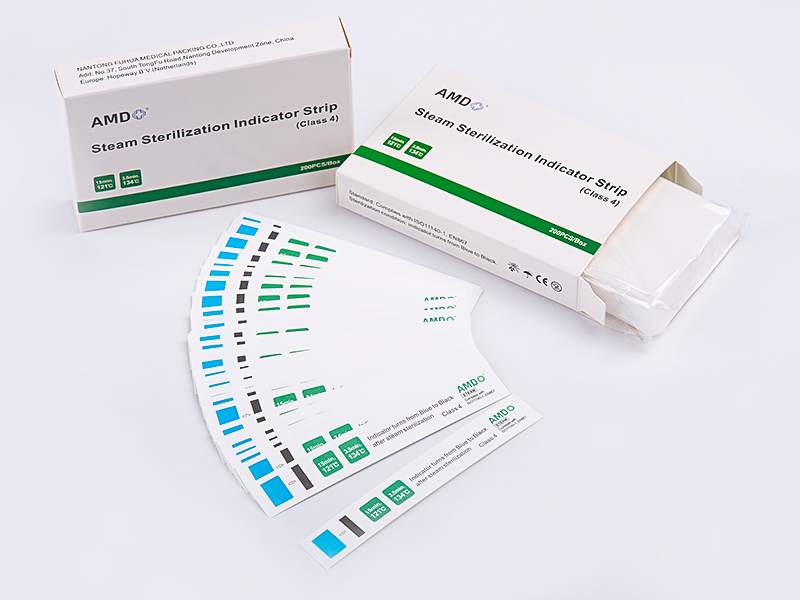
Packaging for terminally sterilized medical devices is covered by international and regional standards that set requirements for materials, barrier performance, labeling and processes that support sterility maintenance. ISO 11607, and related regional standards, is a primary reference for sterile barrier systems and the test methods used to evaluate them. In addition, chemical indicators and the way they report exposure to specific sterilants are governed by standards such as ISO 11140-1. Manufacturers and healthcare providers use these documents to guide material selection, process validation and routine quality control. When selecting a pouch, sterile processing teams should confirm compatibility with the sterilization methods in their facility and verify that indicators and labeling meet local regulatory expectations.
Common sterilization methods and compatibility
Self sealing pouches are intended to work with several established sterilization technologies, but not every pouch is suitable for every process. Typical methods encountered in healthcare settings include:
| Sterilization method | Typical pouch compatibility |
|---|---|
| Steam (autoclave) | Widely supported; many pouches are designed for moist heat cycles. |
| Ethylene oxide (EO) | Pouches compatible with gas sterilization use gas-permeable paper or Tyvek constructions. |
| Low temperature hydrogen peroxide / vapor systems | Specific pouch constructions and validated indicators are required for reliable results. |
| Plasma sterilization | Some Tyvek and specialized pouches may be suitable; manufacturer guidance is essential. |
Practical benefits and operational considerations
From an operational perspective, self sealing pouches can reduce preparation time and minimize reliance on additional packaging equipment. They also make it easier to maintain traceability at the point of care: printed fields on the pouch can hold dates, operator initials and lot information that help with inventory control and recall readiness. In smaller practices where space and resources are constrained, the ability to package items without a heat sealer can be valuable.
At the same time, there are practical caveats. Proper loading technique and filling limits must be observed so that the sterilant reaches all surfaces of an item. Overfilling, folding instruments within the pouch or placing non-compatible materials inside can compromise the sterilization process. Likewise, environmental storage conditions and handling after sterilization will influence how long a packaged item remains acceptable for use; storage policies should follow facility infection prevention guidance.
Indicators, labeling and traceability
A distinguishing feature of clinical sterilization packaging is the use of indicators printed or attached to the pouch. Process indicators show whether a package has been exposed to a sterilization cycle, while biological indicators are part of validation rather than routine packaging. Many pouches also include a space for lot numbers and date stamps to support traceability. Clear, legible labeling helps staff perform visual checks quickly during both processing and before clinical use, and supports compliance with internal and external audits. Users should ensure that indicator chemistry and placement are compatible with their sterilization method and documented validation practices.
Environmental and supply chain themes
As with other single-use products, sterilization pouches raise questions about material selection and waste management. Manufacturers are exploring material options and manufacturing methods that balance barrier performance with recyclability where feasible. Procurement teams increasingly consider supplier quality systems, certifications and the potential for supply continuity when choosing pouch lines. In recent years, attention to supplier audits and regulatory compliance has become a regular part of purchasing conversations, along with considerations about packaging waste streams in the facility.
Choosing the right product for your setting
When evaluating self sealing pouches, sterile processing leaders commonly weigh factors such as sterilant compatibility, visibility of contents, indicator clarity, ease of sealing and the supplier's quality documentation. It is advisable to:
- Match pouch construction to the sterilization processes used at the facility.
- Review the supplier's technical and regulatory documentation to confirm applicable standards and certifications.
- Conduct a small trial run with common instrument types to verify handling, seal integrity and indicator performance in your workflow.
Procurement teams should also coordinate with infection prevention and sterile processing staff so that acceptance criteria reflect clinical needs and regulatory expectations.
Industry outlook and closing note
The self sealing pouch remains a staple of sterile processing because it addresses a clear set of workflow needs: it permits sterilant access, protects instruments after processing and supports rapid packaging in busy environments. Suppliers, including manufacturers that serve clinics and larger institutions, continue to refine materials and printing to meet standards and ease clinical use. For frontline teams, the important considerations are consistent practice, adherence to validated procedures and careful selection of pouch types that match the sterilization methods they use.
Readers seeking specific technical guidance, compatibility tables or material certificates should consult manufacturers' technical documentation and relevant standards directly. For facility-level decisions, involve infection prevention, sterile processing and procurement stakeholders so that product selection is aligned with validated processes and local regulatory requirements.

 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Nederlands
Nederlands











 ‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
 +31 (0)10 254 28 08
+31 (0)10 254 28 08







