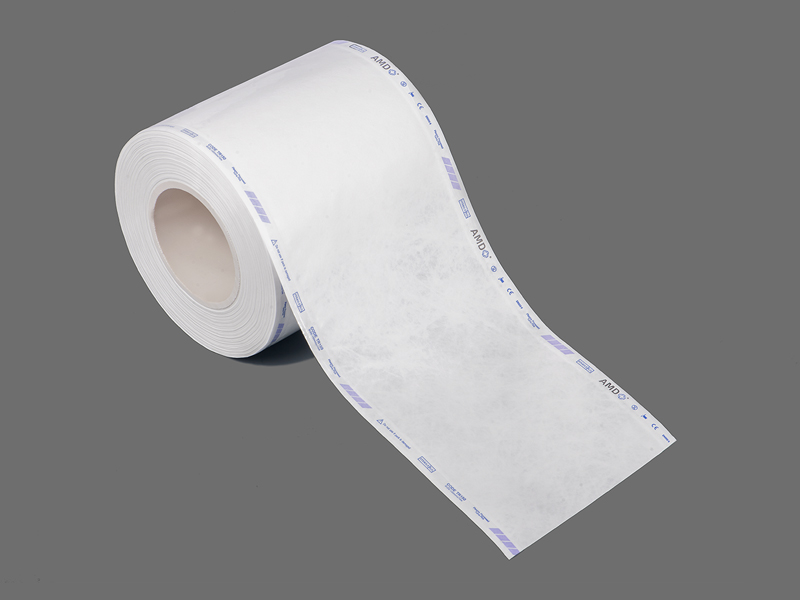
Hospitals, dental clinics, and sterilization units are increasingly looking for packaging options that balance reliability with ease of use. One response to that need is the sterilization gusseted roll offered by Hopeway AMD, a product designed to create flexible, sealed packages for instruments and device sets that do not fit neatly into flat pouches.
Content
- 1 What is a gusseted sterilization roll and how does it differ from flat alternatives?
- 2 Materials and barrier function
- 3 Which sterilization methods are compatible?
- 4 Functional advantages in a real workflow
- 5 Considerations and trade offs
- 6 Typical use cases
- 7 Quality control, indicators, and documentation
- 8 Practical handling tips for staff
- 9 Sustainability and lifecycle thinking
- 10 How to evaluate suppliers
- 11 A compact table for quick comparison
- 12 Realistic expectations
What is a gusseted sterilization roll and how does it differ from flat alternatives?
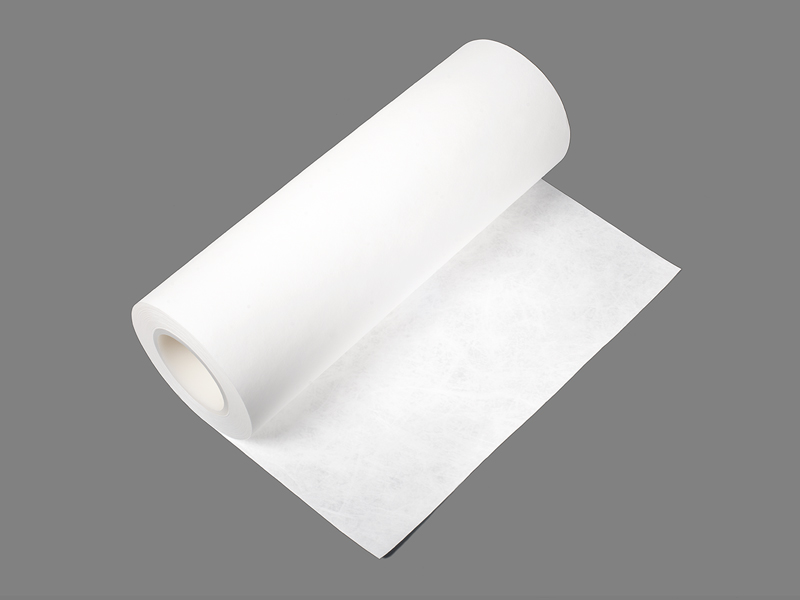
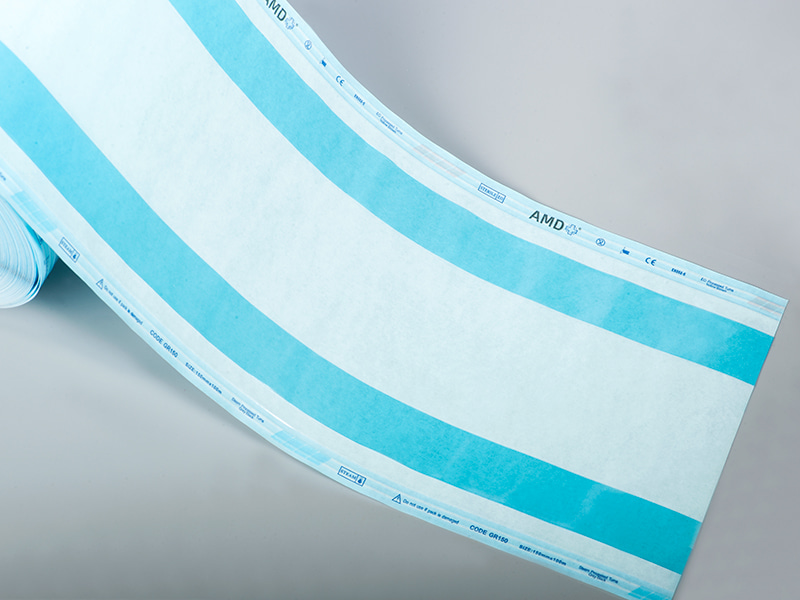
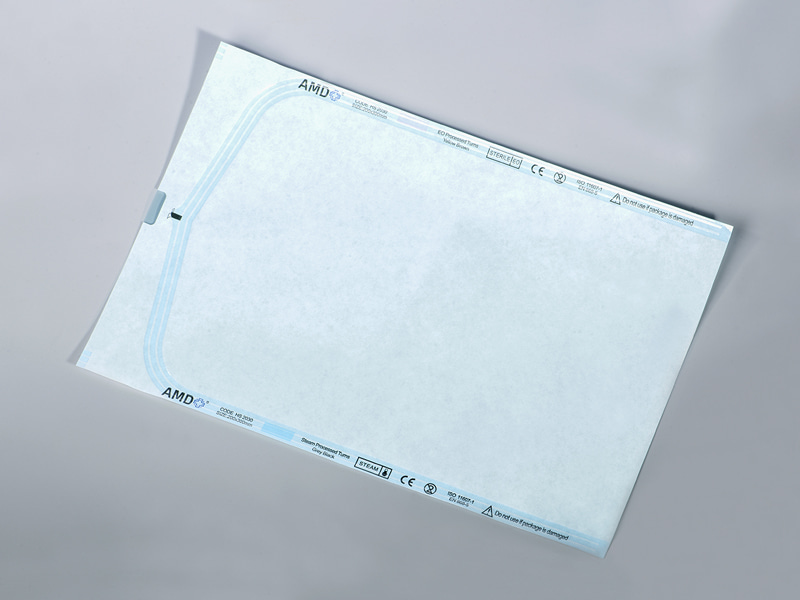
A gusseted sterilization roll is essentially a continuous reel of medical-grade packaging material in which one or both sides are formed with expandable folds, or gussets. When items are wrapped and sealed from the roll, those side folds open up, creating extra internal volume without enlarging the package footprint. That geometry allows teams to accommodate wider, irregular, or bulkier instruments while still producing a sealed sterile barrier comparable to regular pouches. Unlike preformed rigid containers, rolls let staff create packages of custom length on demand, reducing waste for variable sets. Product pages and vendor descriptions highlight the gusseted form as a simple fix for packaging items that would otherwise require multiple pouches or special handling.
Materials and barrier function
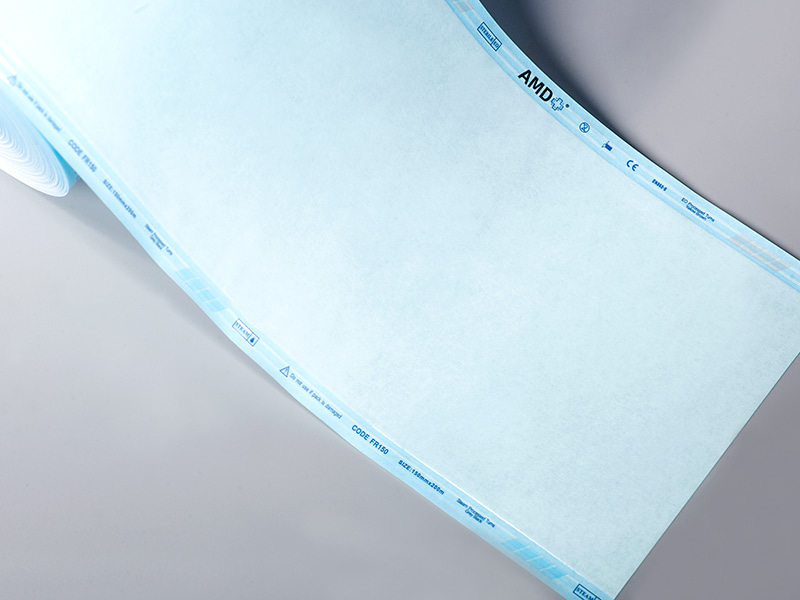
Gusseted rolls intended for sterilization are built as multi-layer composites combining a breathable medical paper and a transparent film layer. The paper provides the microbial barrier required for sterile storage while permitting sterilizing agents to penetrate during the process; the laminated film gives visual inspection capability and mechanical protection during handling and transport. Modern constructions aim to maintain barrier integrity after sterilization and through distribution and storage. Vendor and manufacturer information emphasizes that material choice and lamination quality determine how well the package balances permeability for sterilization and resistance to environmental contamination afterward.
Which sterilization methods are compatible?
Gusseted sterilization rolls are used across several common sterilization modalities, including steam, ethylene oxide (EO), and forms of irradiation. The key requirement is that the package permits the chosen sterilant to reach internal surfaces while maintaining a secure barrier after processing. Many suppliers design rolls for specific method compatibility and advise users to select materials and indicators that match their sterilization cycle. This compatibility is a main reason sterilization departments may prefer rolls for flexible workflows.
Functional advantages in a real workflow
- Adaptable internal volume: The gusset design expands to hold bulkier instruments or instrument clusters that cannot be safely flattened. That reduces the need to split sets across multiple packages or to improvise with oversized pouches.
- On-demand custom lengths: Because the product comes as a continuous reel, staff can cut the exact length needed for a tray or instrument, reducing unused material and streamlining wrapping steps.
- Improved visibility and handling: Transparent film sections let technicians visually confirm contents and orientation before sealing and after sterilization, which speeds inspection.
- Simplified inventory: One roll type can cover a range of items, which can reduce the number of SKUs a sterile processing department needs to maintain.
- Traceability options: Many manufacturers support labeling areas or printing on the film for lot numbers and sterilization dates, assisting documentation and recall-readiness.
These functional strengths are often cited by facilities that aim to reduce packing time while maintaining consistent barrier performance.
Considerations and trade offs
No product is a universal solution; choosing a gusseted roll should be an informed decision based on workflow, instruments, and sterilization policy.
- Sealing technique: Proper heat sealing or closure is essential to maintain sterility. Staff must follow validated sealing parameters and use compatible equipment to avoid compromised seals.
- Material selection: Different films and papers vary in strength, breathability, and puncture resistance. Facilities should select a construction suitable for their instruments and handling conditions.
- Storage conditions: Like other sterile barriers, packages must be stored in controlled conditions to maintain sterility through the intended shelf period. Humidity, temperature swings, and rough handling can shorten the practical life of a sealed pack.
- Regulatory and standards compliance: Choose materials and suppliers that demonstrate conformity with applicable sterile packaging standards and quality systems. Many reputable manufacturers publish compliance information and quality certifications that buyers can review.
Typical use cases
Gusseted rolls find practical use in multiple settings:
- Central Sterile Supply Departments (CSSD/Central Sterile): For instrument sets that include bulky items or irregular trays, rolls offer a quick means to form single, sealed packages.
- Operating theatres and ambulatory surgical centers: Where quick turnaround and reduced storage of preformed pouches are desirable, rolls allow customized packs to be prepared near use time.
- Dental practices and specialty clinics: Instruments and handpieces with nonstandard shapes can be packaged efficiently without excessive overwrap.
- Manufacturers and distributors: When shipping assembled device kits that require terminal sterilization, gusseted reels can provide a flexible packaging option that supports sterilization and transit.
Quality control, indicators, and documentation
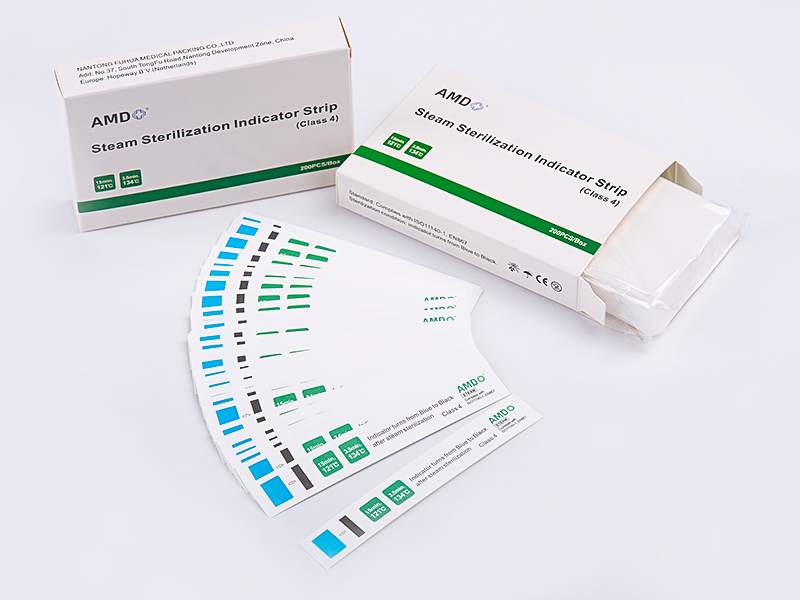
A robust sterile processing program pairs packaging with appropriate chemical or physical indicators and clear labeling practices. Chemical indicators that change color when exposed to a sterilization cycle type are frequently incorporated into pouch or roll systems; their placement and interpretation should follow facility protocols. For traceability, manufacturers often provide space on the film or paper for production lot numbers, expiry information, and sterilization dates, which helps with record keeping and product recalls if needed. Reviewing vendor documentation and requesting sample packs for validation runs can reduce surprises when adopting a new roll product.
Practical handling tips for staff
- Train all users on correct sealing procedures and on visual inspection criteria for the finished seal and package.
- Use validated sealing devices and monitor their performance regularly. Sealer maintenance and routine checks reduce the risk of weak sealing.
- When preparing larger or oddly-shaped instruments, allow a small margin for internal movement that could stress the package; use cushioning or instrument wraps as needed.
- Mark packages clearly and consistently to support sterile stock rotation and usage tracking.
- If your department uses multiple sterilization methods, segregate packages or label them to indicate the intended sterilization process so that they are not inadvertently processed under the wrong cycle.
Sustainability and lifecycle thinking
Manufacturers and buyers are increasingly mindful of environmental impact. Some suppliers have explored material choices and manufacturing processes that reduce waste or allow easier recycling of secondary packaging while maintaining medical-grade performance. When assessing options, procurement teams should weigh total lifecycle impacts: how much material is used per instrument, whether fewer packages are needed overall, and how storage and transport efficiencies change with a switch to gusseted rolls. Hopeway AMD and other vendors have published commentary on barrier materials and sustainability considerations as the market evolves, which can inform decisions at the facility level.
How to evaluate suppliers
Choosing a vendor for sterile packaging requires attention to more than price:
- Quality systems: Prefer suppliers that operate under recognized quality management systems and who can document their manufacturing controls.
- Standards compliance: Look for evidence of compliance with relevant packaging and sterilization standards, which can be a helpful shorthand for basic acceptability.
- Technical support: A supplier that provides validation assistance, sample runs, and troubleshooting support can reduce the burden on internal teams.
- Customization and inventory flexibility: If your facility needs specific widths, gusset depths, or printing options, assess whether the supplier can deliver small-batch.
A compact table for quick comparison
| Topic | What to look for | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Material construction | Breathable medical paper + laminated film | Balances sterilant penetration and post-process barrier |
| Gusset design | Single or double side gussets, expandable folds | Allows packaging of bulky or irregular instruments |
| Sealing compatibility | Heat-seal or peelable closure options | Ensures consistent sterile barrier if sealer validated |
| Traceability | Areas for lot numbers and dates | Supports inventory control and recall readiness |
| Vendor support | Validation samples and technical guidance | Eases adoption and reduces implementation risk |
(Use this table as a checklist when comparing roll options against facility needs.)
Realistic expectations
Switching or adding a gusseted roll to a department's supply mix is primarily an operational choice. It offers proven practical benefits in terms of flexibility and efficiency, but those gains rely on good process control, staff training, and appropriate selection of materials for the sterilization methods in use. Facilities that invest in validation and that align selection with instrument handling patterns tend to realize smoother implementation and more predictable outcomes.
Gusseted sterilization rolls represent a pragmatic option for settings that must package items of varying shapes and sizes without complicating inventory or increasing handling time. When chosen and used thoughtfully—paired with validated sealing equipment, correct sterilization indicators, and consistent handling protocols—these rolls can simplify many packaging tasks while preserving the sterile barrier required for patient safety. For teams exploring alternatives to flat pouches or looking to streamline packaging of larger sets, a gusseted reel is worth a practical trial supported by vendor samples and a short validation exercise.
If you want to review product details or request samples from the manufacturer discussed here, you can find more information and technical documentation on the Hopeway AMD website.

 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Nederlands
Nederlands











 ‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
 +31 (0)10 254 28 08
+31 (0)10 254 28 08







