With the increasing global demand in the medical industry for sterilization management and instrument safety, healthcare facilities are imposing higher standards for controllability and traceability in sterilization processes. Against this backdrop, Steam Indicator Strips/Tape has gained wide attention in the industry as an essential tool for verifying sterilization effectiveness. Its unique material properties, reliable indication mechanism, broad applicability, and strong environmental adaptability make it an irreplaceable component in medical instrument sterilization management. This article will provide an in-depth analysis of the basic concept, materials, applications, operation, accuracy, storage and shelf life, safety considerations, and environmental adaptability of Steam Indicator Strips, exploring their value and development trends in modern healthcare.
Content
- 1 1. What Are Steam Indicator Strips/Tape and How Do They Work?
- 2 2. Differences Between Steam Indicator Strips and Steam Indicator Tape
- 3 3. Material Composition and Characteristics of Steam Indicator Strips/Tape
- 4 4. Applications and Uses
- 5 5. Operation and Accuracy
- 6 6. Storage and Shelf Life
- 7 7. Safety and Operational Considerations
- 8 8. Environmental Adaptability
- 9 9. Industry Trends and Future Outlook
1. What Are Steam Indicator Strips/Tape and How Do They Work?
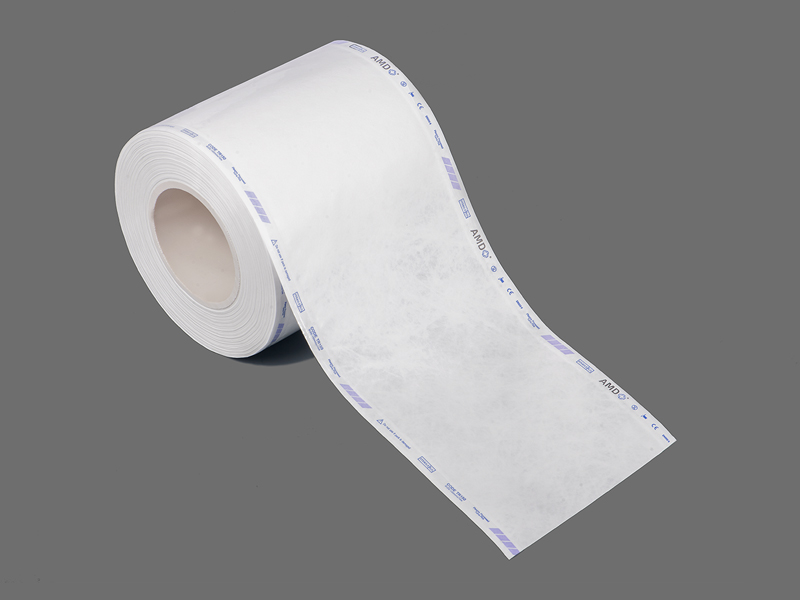
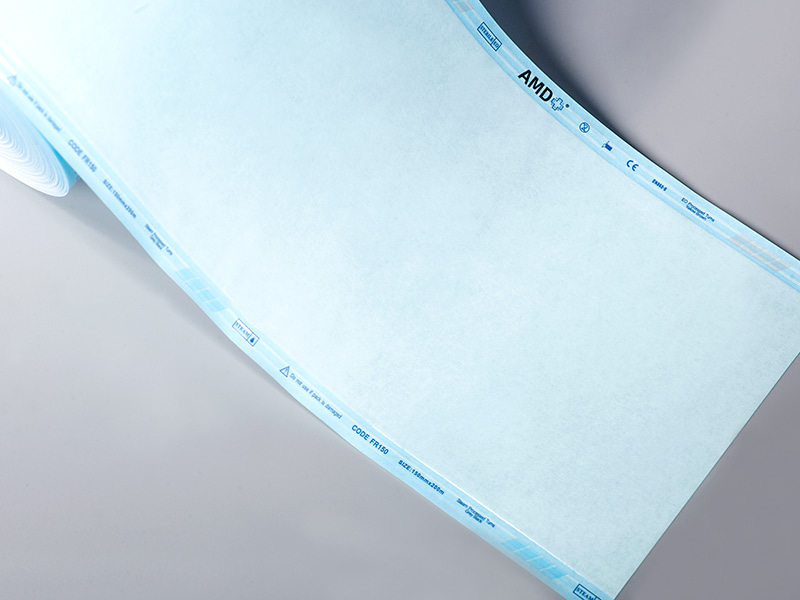
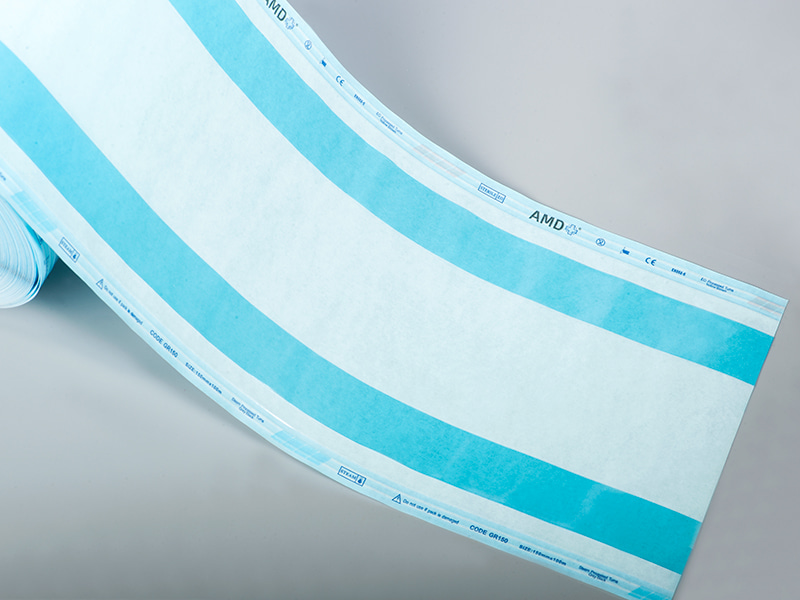
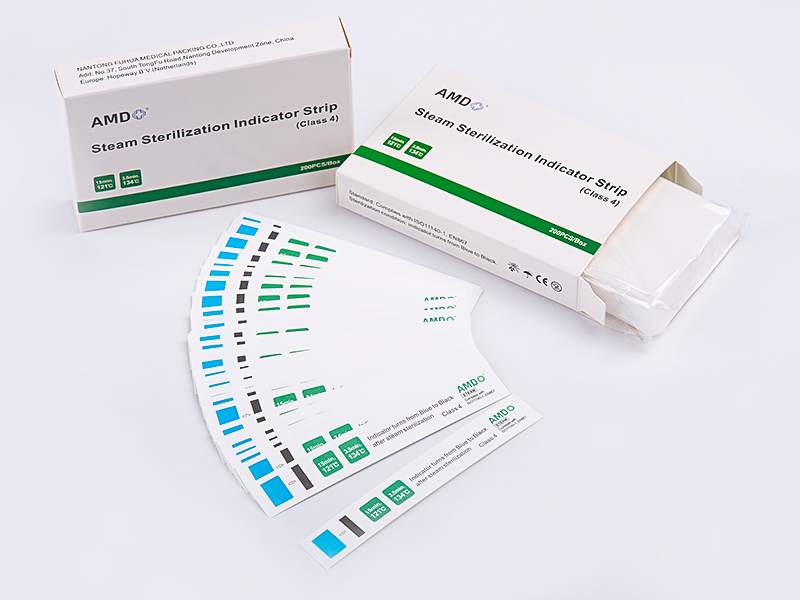
Strips and Steam Indicator Tape are specially designed tools for monitoring the effectiveness of steam sterilization. Their working principle is based on a chemical reaction triggered by temperature, humidity, and steam, causing a visible color change in the indicator area, signaling whether sterilization has been successfully completed. Indicator strips are typically placed inside sterilization packages or trays, while indicator tape is often used on seals or the exterior of packaging to ensure steam penetration throughout the package.
The speed and extent of the color change can reflect the temperature, humidity, and steam penetration during the sterilization process, providing healthcare facilities with a direct and rapid means of sterilization verification.
2. Differences Between Steam Indicator Strips and Steam Indicator Tape
Although both Strips and Indicator Tape are used for sterilization verification, they differ in usage and application scenarios:
| Type | Usage Method | Application Scenario | Indication Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steam Indicator Strips | Placed inside packaging or trays | Monitoring internal steam penetration and sterilization effectiveness | Internal indication, shows full sterilization process |
| Steam Indicator Tape | Applied to the exterior or seal of packaging | Packaging sealing and quick surface verification | Surface indication, convenient for quick checks |
From the table, it is clear that indicator strips are more suitable for monitoring the internal sterilization status of instruments, while indicator tape is more convenient for routine operations and seal verification.
3. Material Composition and Characteristics of Steam Indicator Strips/Tape
The core function of Strips and Tape is to accurately reflect the sterilization process, making material selection crucial. Generally, they consist of three layers: the substrate layer, the chemical indicator layer, and the protective layer, each with different functions and performance requirements.
1. Substrate Layer
The substrate provides structural support for the strip or tape, determining its mechanical strength, flexibility, and high-temperature resistance. Common substrates include:
High-Temperature Nonwoven Material
Made from polypropylene or high-density polyethylene fibers, this material is lightweight, tear-resistant, and puncture-resistant. The nonwoven fiber structure allows steam to penetrate while maintaining microbial barrier properties.
High-Temperature Resistant Paper
Specially treated paper substrates can withstand high-temperature steam sterilization while maintaining breathability and flexibility. Paper is commonly used for disposable sterilization indicator strips and is relatively low-cost.
Tape Substrate
For indicator tape, heat-resistant films or paper substrates are used to ensure firm adhesion under high temperature and humidity while providing accurate steam indication at seal points.
2. Chemical Indicator Layer
This is the core functional layer of strips and tape, primarily responsible for displaying sterilization status through chemical reactions:
Chemical Indicator Ink
The ink applied in this layer changes color under specific temperature and humidity conditions—for example, from light to dark, or from yellow to brown—indicating whether the sterilization process meets requirements.
Reaction Mechanism
The chemical components are sensitive to steam, temperature, and pressure, ensuring that the color change is intuitive and easy to read. Different types of strips may use different chemical formulations to suit various sterilization cycles and equipment requirements.
Safety
All chemical indicator components must comply with medical safety standards, posing no risk of contaminating medical instruments or harming operators.
3. Protective Layer
The protective layer usually covers the chemical indicator layer to enhance durability and operational safety:
Transparent Coating or Film
Prevents the chemical layer from being rubbed off during handling, storage, or sterilization while ensuring that color changes remain clearly visible.
Moisture Protection
For indicator strips, the protective layer reduces interference from external humidity, improving the accuracy of results.
Enhanced Mechanical Strength
Prevents strips or tape from breaking or being damaged during transport and handling, ensuring the reliability of sterilization verification.
4. Summary of Material Characteristics
| Layer | Material Type | Function and Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Layer | Nonwoven fiber / high-temp paper / tape film | Provides mechanical strength and flexibility, allows steam penetration |
| Chemical Indicator Layer | Special chemical ink | Sensitive to steam, temperature, and pressure; displays color change; safe and non-toxic |
| Protective Layer | Transparent coating / film | Anti-abrasion, moisture protection, enhanced durability, ensures accurate reading |
Through the rational combination of these layers, Steam Indicator Strips can accurately display sterilization effectiveness under high-temperature and high-humidity conditions while maintaining operational safety, high mechanical strength, and long-term reliability. This multi-layer structure is a key reason why they are widely used for sterilization verification of surgical instruments, disposable medical supplies, and other sensitive medical devices.
4. Applications and Uses
Strips and Steam Indicator Tape are primarily used to monitor and verify the effectiveness of steam sterilization processes. Their applications are wide-ranging, covering everything from disposable medical supplies to complex medical instruments. Correct use of these indicators not only ensures sterilization effectiveness but also enhances quality management and operational efficiency in healthcare facilities.
1. Sterilization Verification for Surgical Instruments
Surgical instruments such as scalpels, scissors, forceps, clamps, and endoscopic accessories have very high requirements for sterilization environments.
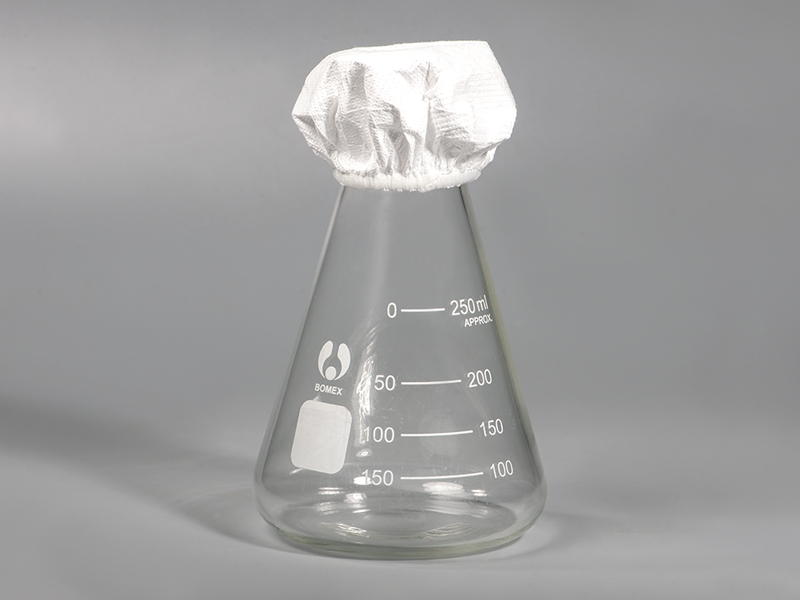
Internal monitoring: Indicator strips can be placed in corners or hard-to-reach areas inside instrument trays, ensuring every instrument is exposed to steam.
Sterilization verification: Color changes provide a visual confirmation that instruments have reached the required sterilization temperature and pressure, ensuring safe use.
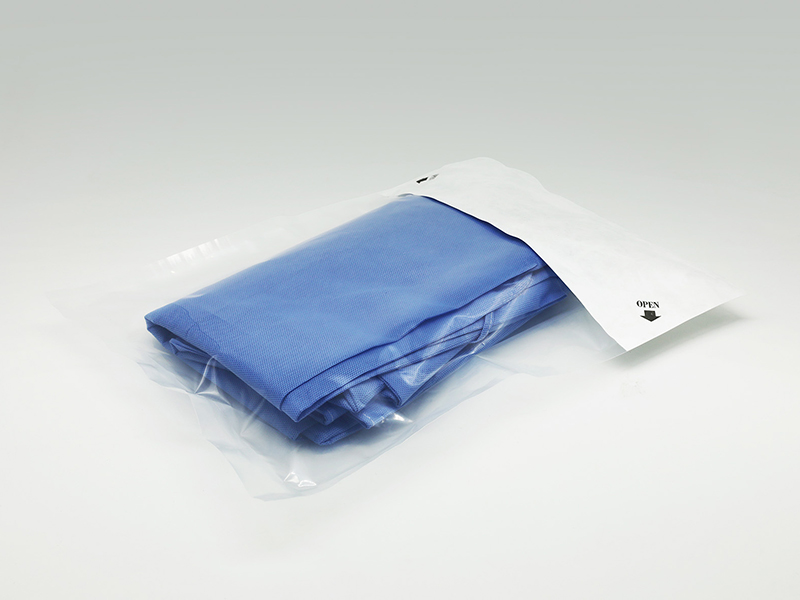
2. Disposable Medical Supplies
Disposable items such as syringes, catheters, gloves, and masks are typically sterilized in batches.
Package seal monitoring: Indicator tape is applied to external seals to quickly determine whether packaging has undergone sterilization.
Internal verification: Critical items can also include internal indicator strips to ensure that each packaged unit reaches sterilization conditions.
3. Instrument Trays and Packaging
In hospitals and laboratories, instruments are often placed in trays for high-temperature steam sterilization:
Internal placement: Indicator strips can be positioned in different areas inside trays to monitor steam penetration and evenness of temperature and humidity.
Multi-point verification: Placing multiple strips at different locations allows comprehensive monitoring, reducing the risk of partial under-sterilization.
4. Packaging Seal Verification
Indicator tape is widely used on sterilization package seals:
Quick check: The color change on the tape provides a rapid indication of effective steam sterilization.
Ease of operation: Enables healthcare personnel to quickly confirm sterilization status in busy environments, improving workflow efficiency.
5. Laboratory and Specialized Applications
In laboratories, dental clinics, and high-risk medical environments, Tape also play a critical role:
Sample sterilization: Used for petri dishes, reagent bottles, or small equipment verification.
High-risk instruments: Can be placed in specialized sterilization packages to ensure that the entire cycle meets sterilization requirements.
6. Multi-level Sterilization Monitoring
Modern healthcare facilities often use indicator strips and tape together to form multi-level sterilization verification systems:
Internal indicator strips: Monitor steam penetration inside instruments.
External indicator tape: Provides a rapid indication of overall packaging sterilization.
Combined use: Offers more reliable verification for high-value or sensitive medical instruments.
Summary of Applications:
| Application Category | Usage Method | Function & Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical Instruments | Internal placement of strips | Monitors steam penetration, ensures instruments remain sterile |
| Disposable Supplies | Internal strips + seal tape | Comprehensive verification of package sterilization |
| Instrument Trays | Multi-point placement of strips | Checks sterilization uniformity, prevents partial under-sterilization |
| Packaging Seals | External application of tape | Quick sterilization check, easy to use |
| Laboratory / Specialized Equipment | Internal placement of strips or tape | High-risk sample sterilization verification, ensures safety |
Through these applications, Tape not only improve controllability in sterilization management but also provide reliable assurance for instrument safety and patient safety.
5. Operation and Accuracy
Proper operation is key to ensuring that indicator strips and tape accurately reflect sterilization effectiveness. Main operational considerations include:
1.Placement: Strips should be positioned inside sterilization packs or in hard-to-reach corners to monitor steam penetration.
2.Avoid direct contact with instruments: Prevent contamination of instruments by chemical indicator ink.
3.Observation time: Color changes should occur within the specified timeframe; delays may affect readings.
4.Repeated verification: High-value or sensitive instruments can be monitored with multiple strips to increase accuracy.
Correct operation effectively prevents false positives or false negatives, ensuring reliable sterilization records.
6. Storage and Shelf Life
Indicator strips and tape must be stored correctly before use to maintain stable performance:
Storage environment: Keep in a dry, dark, and room-temperature environment.
Avoid moisture: Excessive humidity may prematurely trigger the chemical ink, affecting accuracy.
Shelf life: Typically indicated on the packaging; expired products may cause misreading.
Rotation: Use a first-in-first-out (FIFO) principle to ensure strips and tape are always in condition.
7. Safety and Operational Considerations
The safety of Strips is reflected in several key aspects:
Non-toxic and Safe: The materials and chemical indicator inks do not contaminate medical instruments or pose health risks to operators.
High Temperature and Pressure Resistance: They do not break or release harmful gases during the sterilization process.
Proper Operation: Strict adherence to operating instructions when placing the strips ensures that human factors do not cause abnormal readings.
Proper operation and appropriate usage environments ensure that sterilization verification remains safe and reliable.
8. Environmental Adaptability
Tape demonstrate strong environmental adaptability, maintaining performance under varying conditions:
Temperature Range Adaptability: Effective across standard steam sterilization temperature ranges.
Humidity Adaptability: Accurately indicates sterilization effectiveness even in high-humidity environments.
Load Adaptability: Effectively reflects sterilization status regardless of load density or packaging type.
Compatibility with Other Indicators: Can be used alongside chemical or biological indicators to form multi-level sterilization verification systems.
Illustration: Placement positions and color change demonstration of steam indicator strips.
9. Industry Trends and Future Outlook
With the increasing diversity of medical devices and higher standards for sterilization management, demand for Strips continues to grow. Future development trends include:
Intelligent Systems: Integration with barcodes or RFID for automatic sterilization data recording and tracking.
Sustainability: Development of environmentally friendly, recyclable materials to reduce medical waste burden.
Multi-functionality: Incorporation of temperature and humidity monitoring capabilities to improve the accuracy and reliability of sterilization verification.
Global Standardization: Further compliance with international ISO, ANSI, and regional regulatory requirements to enhance cross-regional medical logistics safety.
As healthcare facilities place greater emphasis on sterilization safety, efficiency, and traceability, the application prospects for Tape are broad, and they are expected to play an increasingly important role in modern sterilization management.
Steam Indicator Strips/Tape demonstrate significant advantages in material performance, operational accuracy, storage safety, environmental adaptability, and regulatory compliance. They provide a reliable and intuitive method for verifying medical instrument sterilization, while also supporting healthcare facilities in improving sterilization management efficiency and safeguarding patient safety. With ongoing technological advancements and continuous refinement of industry standards, the application value of Tape will continue to grow, and they are expected to occupy a central role in the field of medical sterilization monitoring.

 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Nederlands
Nederlands











 ‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
 +31 (0)10 254 28 08
+31 (0)10 254 28 08







