In the field of medical sterilization, ethylene oxide (EO) sterilization has become one of the mainstream methods for medical devices due to its strong low-temperature penetration and broad material compatibility. However, how can the effectiveness of the sterilization process be monitored in real time? How can it be ensured that every instrument meets sterility requirements? Developed by Hopeway AMD, the EO Indicator Strips (ethylene oxide sterilization chemical indicator cards) provide intuitive visual verification of the sterilization process through precise chemical color change reactions, becoming a true “process monitoring guardian” for hospitals, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and third-party sterilization centers.
Content
- 1 Classification of Chemical Indicators and Core Functions
- 2 Critical Role in EO Sterilization
- 3 Core Technology Principles and Performance Advantages
- 4 Industry Applications and Quality Control
- 5 Sensitivity and Stability: A "Magnifier" for Subtle Differences
- 6 Differentiated Advantages Compared with Steam Indicator Strips
- 7 Environmental Adaptability and Operational Guidelines
- 8 Application Value: From Compliance to Risk Control
Classification of Chemical Indicators and Core Functions
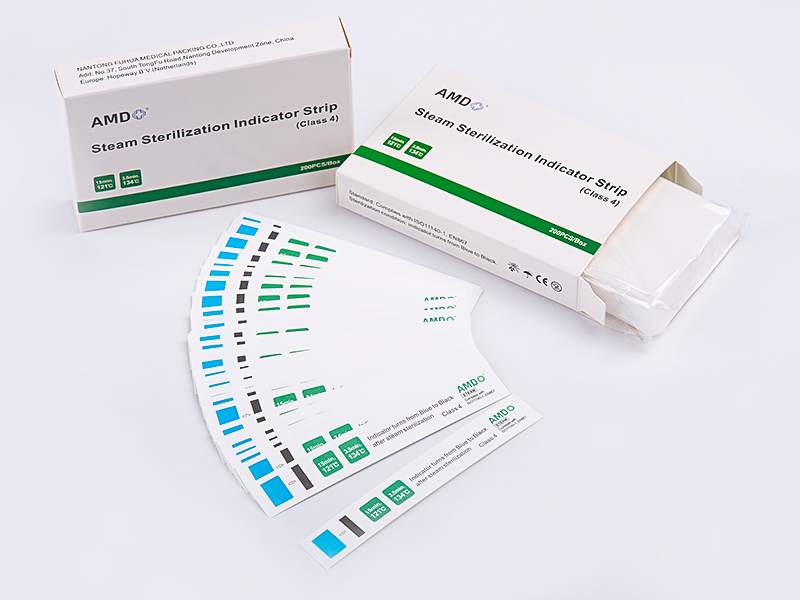
EO Strips fall under Class 4 chemical indicators (process indicators). Their core function is to visually reflect whether key sterilization parameters (such as EO concentration, temperature, and humidity) have reached preset thresholds through specific chemical reactions. Unlike Class 1 indicators, which only show whether an item has been exposed to the sterilization process, Strips verify whether sterilization conditions have been fully achieved, bridging the gap left by biological monitoring that is time-consuming and unable to provide real-time feedback.
Critical Role in EO Sterilization
During the EO sterilization process, the indicator cards play a vital role through the following mechanisms:
1.Sensitive Coating Reaction: The indicator area contains a customized chemical dye formulation. When exposed to an effective concentration of EO gas under suitable temperature and humidity conditions, the dye undergoes an irreversible chemical reaction.
2.Multi-parameter Synergistic Verification: The indicator responds not only to EO concentration but also to temperature (±2℃) and relative humidity (±5%), reducing the risk of “false positives” caused by a single parameter meeting the standard.
3.Standardized End-point Interpretation: After sterilization, the indicator area changes from the initial color (e.g., yellow) to a standardized endpoint color (e.g., green). Operators can quickly compare the result with a reference color chart for accurate reading.
| Key Parameter | Response Threshold | Color Change Mechanism |
| EO Concentration | ≥ Minimum Effective Concentration | Dye molecular structure reconfiguration |
| Temperature | Sterilization cycle integrated temperature reached | Activation of thermo-sensitive catalyst |
| Humidity | Maintained above RH critical value | Expansion of hydrophilic substrate triggers reaction |
Core Technology Principles and Performance Advantages
The core technology of the indicator card lies in its precisely engineered chemical formulation:
1.Molecular-Level Response Mechanism: Special organometallic complexes are used as indicators. When exposed to an effective concentration of EO gas, the molecular structure undergoes irreversible rearrangement.
2.Temperature and Humidity Compensation System: An internal buffering mechanism eliminates errors caused by environmental fluctuations.
3.Gradient Color Development Technology: The indicator presents differentiated color changes according to the completeness of sterilization.
Industry Applications and Quality Control
In medical device manufacturing processes, EO have become a critical component of quality control. Their main application scenarios include:
1.Process Validation: Used for periodic verification and daily monitoring of sterilization processes.
2.Load Verification: Placed in the challenging locations within the sterilization chamber to confirm uniform sterilization.
3.Batch Release: Serves as a rapid release basis prior to biological monitoring results.
"In practical use, we find that this indicator card is particularly well-suited for sterilization verification of complex instruments," said the director of the CSSD at a hospital. "For example, for luminal devices such as endoscopes, traditional monitoring methods are often unable to provide comprehensive coverage."
Sensitivity and Stability: A "Magnifier" for Subtle Differences
Compared with traditional sterilization labels,Strips demonstrate significantly enhanced sensitivity:
Detection of Short-Term Fluctuations: Even if EO concentration temporarily drops below the threshold (e.g., due to equipment fluctuations), the indicator area may display "mottled color changes,"signaling incomplete sterilization.
Strong Color Stability: The post-reaction color remains stable at room temperature for several months, meeting the requirements for sterilization record archiving (light-protected storage is recommended to extend color retention).
Anti-interference Design: A special packaging process prevents false results caused by water vapor, residual disinfectants, or other interfering factors.
Differentiated Advantages Compared with Steam Indicator Strips
Although steam sterilization indicator strips (such as the Bowie-Dick test) also rely on chemical color change, the two differ fundamentally:
| Comparison Dimension | EO Indicator Strips | Steam Sterilization Indicator Strips |
| Core Reactive Substance | Ethylene oxide gas | Saturated steam temperature |
| Humidity Dependence | High | Low (primarily temperature-responsive) |
| Applicable Scenarios | Flexible endoscopes, disposable catheters, and other EO-sensitive materials | Metal instruments, textiles, and other high-temperature-resistant items |
Environmental Adaptability and Operational Guidelines
Temperature and Humidity Effects and Responses
Low-temperature, high-humidity environments: Reaction speed slows down, requiring extended exposure time (Hopeway AMD provides models adapted for different climate zones).
High-temperature, low-humidity environments: May cause false color changes; it is recommended to cross-check results with temperature and humidity sensors inside the sterilization chamber.
Key Points for Use and Storage
1.Before sterilization: Place the indicator card at the challenging position for sterilization (e.g., inside lumens).
2.After sterilization: Read immediately to avoid interference from condensation.
3.Storage conditions: Store in a dry environment at 10–30℃, away from organic solvents.
4.Waste disposal: Dispose of as medical waste (non-reacted cards should be re-sterilized before disposal).
Application Value: From Compliance to Risk Control
EO Indicator Strips have been widely applied in:
Implant sterilization: Serving as a rapid release basis before biological monitoring.
Sterilization process validation: Supporting optimization of EO exposure time, dosage, and other parameters.
Cross-border transport supervision: Providing visual compliance proof for sterilized packaging.
With rising medical quality standards and continuous innovation in sterilization technologies, these products will continue to play a critical role in safeguarding healthcare safety. Hopeway AMD remains committed to ongoing R&D investment, delivering more advanced and reliable sterilization monitoring solutions for the global healthcare industry.

 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Nederlands
Nederlands











 ‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
 +31 (0)10 254 28 08
+31 (0)10 254 28 08







