Content
- 1 I. What Is a "Sterilization Flat Roll"?
- 2 II. What Makes a Truly Reliable Sterilization Flat Roll — Material, Seal, or Sterilization Compatibility?
- 3 III. What Is the Difference Between a Standard Sterilization Pouch and a Gusseted Roll?
- 4 IV. How to Choose the Right Packaging for Different Scenarios?
- 5 V. Why Is the Flat Roll Gaining More Attention in the Industry?
- 6 VI. Three Recommendations from Hopeway AMD for Packaging Decision-Makers
- 7 VII. Industry Outlook
I. What Is a "Sterilization Flat Roll"?
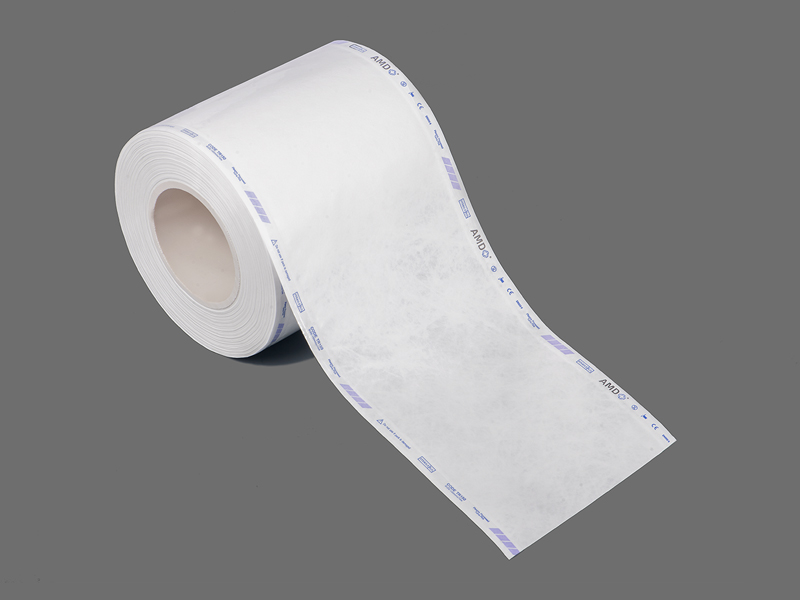
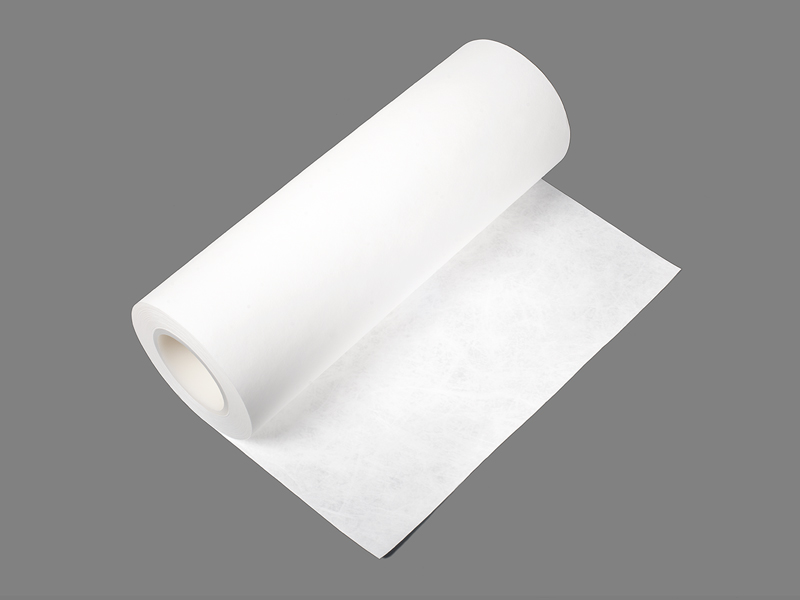
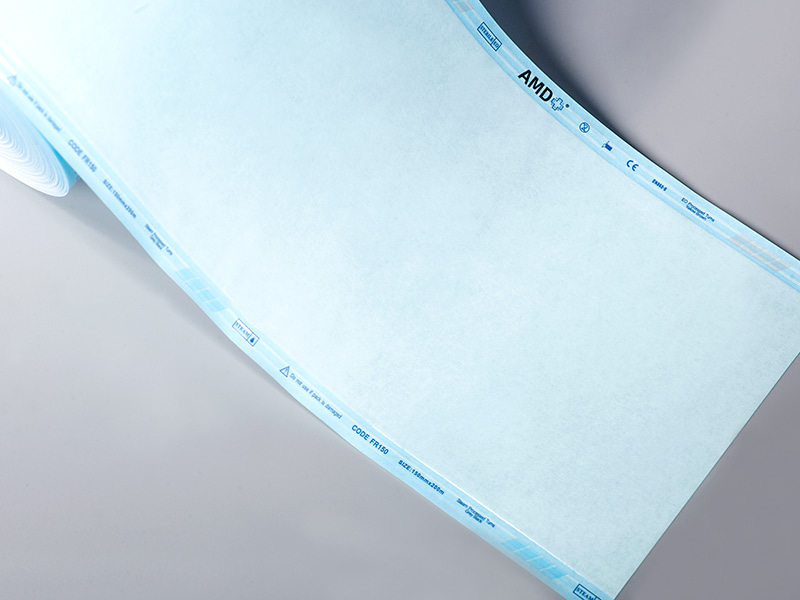
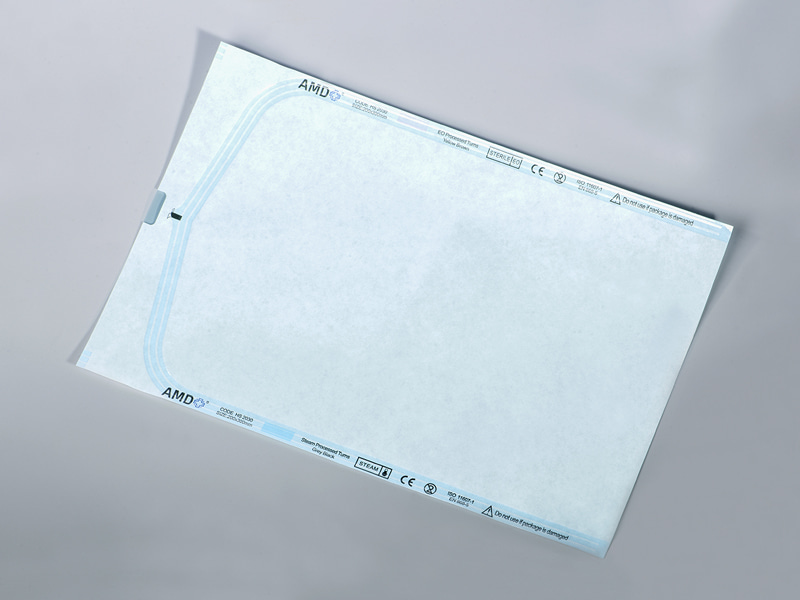
A Flat Roll refers to a flat-type sterilization packaging material supplied in roll form. It consists of a continuous sheet that can be cut to the required length, sealed by heat or other methods, and then subjected to sterilization. According to industry information, a Flat Roll is typically made from medical-grade paper combined with transparent plastic or reinforced film — such as multilayer PP/PET laminated film with medical paper.
Its purpose is to allow sterilizing agents (such as steam or ethylene oxide) to penetrate effectively while maintaining a sterile barrier during storage, transportation, and before opening.
From a material structure perspective, it generally has the following features:
Medical paper (e.g., 60 gsm or 70 gsm) on one side, providing both breathability and microbial barrier performance.
Transparent or semi-transparent film (such as CPP/PET multilayer co-extruded film) on the other side, allowing visibility of the contents and preventing packaging errors.
Chemical indicators printed on the paper side (e.g., steam or ethylene oxide indicators) to verify whether the sterilization process has been completed successfully.
Therefore, when considering the Flat Roll within the context of sterilization and packaging workflows, it serves as a flexible, efficient, and adaptable packaging medium for a wide range of medical devices and instruments.
II. What Makes a Truly Reliable Sterilization Flat Roll — Material, Seal, or Sterilization Compatibility?
In industry discussions, these three aspects are often raised repeatedly when evaluating the reliability of sterilization packaging materials. The following analysis examines each factor in depth and provides a suggested order of importance based on practical application.
1. Material
Material is the foundation. Packaging must remain stable under sterilization conditions — it should not tear, deform, or release harmful substances due to heat, humidity, or chemical exposure.
As noted in industry guidelines:
"The material you select needs to accommodate each of these three influencers (device + sterilization process + packaging design) in order to make it into the market successfully."
Additionally, technical reports emphasize that Flat Rolls "can withstand the temperature ranges of steam sterilization and ethylene oxide sterilization while maintaining material stability and flexibility."
This means the material must provide:
High temperature resistance
Chemical stability
Gas or steam permeability (for sterilant penetration)
Strong microbial barrier properties
If the base material fails, even the sealing process cannot compensate for that weakness.
2. Seal / Closure
The sealing mechanism determines the integrity of the packaging. Even with high-quality materials, a poor seal can to microbial contamination or sterilization failure. Sterilization packaging must fulfill three primary functions:
Allow sterilant penetration to all surfaces of the instrument;
Maintain sterility after the sterilization process until the point of use;
Permit aseptic presentation and handling.
Seal quality includes factors such as heat-seal strength, number of sealing lines (e.g., triple-line seals), seal continuity, and compatibility with sealing machinery. Some Flat Roll products feature "triple band seals" to enhance package integrity — highlighting how critical this factor is in ensuring barrier protection.
3. Sterilization Compatibility
This refers to whether the packaging materials and sealing properties match the sterilization method being used (e.g., steam, ethylene oxide, or low-temperature processes). If the packaging is incompatible with the sterilization process, sterility cannot be guaranteed and the structure may be damaged.
Industry observations note:
"Although they may look similar, when a pouch is used in the wrong sterilization process, a failure is likely to occur."
One of the advantages of the Flat Roll design is its "compatibility with various sterilization techniques." This flexibility makes it suitable for different healthcare and laboratory environments.
Priority Order
In summary, if the three key factors are ranked by importance, the sequence would be:
Material → Seal → Sterilization Compatibility.
The reasoning is:
If the material cannot withstand sterilization conditions, the rest is irrelevant.
Even with good material, poor sealing can compromise sterility.
When both material and sealing are reliable, sterilization compatibility demonstrates its full value.
In practice, however, all three must be evaluated together — a truly reliable sterilization packaging system requires the right balance of all factors.
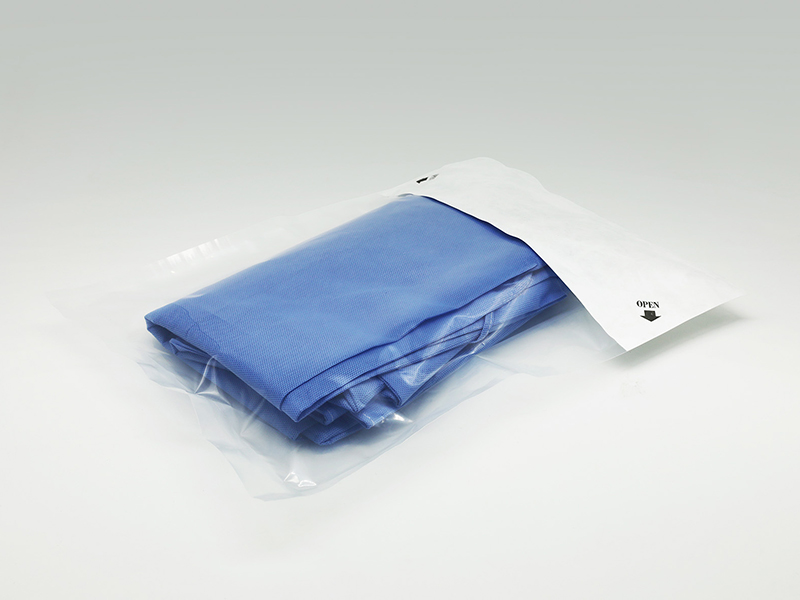
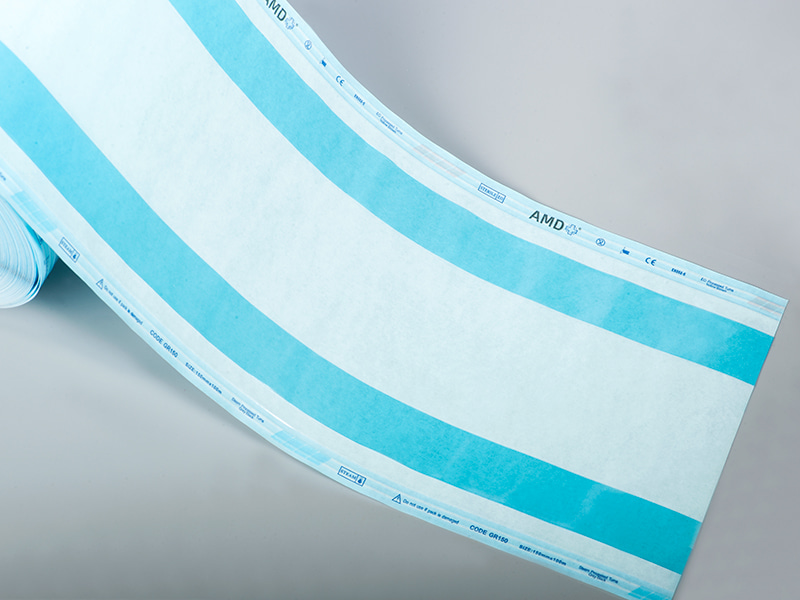
III. What Is the Difference Between a Standard Sterilization Pouch and a Gusseted Roll?
In terms of packaging structure, the industry often compares Sterilization Pouches, Flat Rolls, and Gusseted Rolls.
The table below summarizes their key differences:
| Feature Dimension | Standard Sterilization Pouch | Gusseted Roll |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Pre-made bag with fixed dimensions; one end sealed by heat or self-sealing | Roll material that can be cut to desired length; forms a bag after sealing, with side gussets to accommodate volume variation |
| Loading Flexibility | Suitable for fixed-size instruments or small components | Better suited for bulky, irregularly shaped, or multi-component instruments |
| Material Cutting Efficiency | Minimal cutting required, fixed usage | Flexible cutting reduces waste, but sealing must match the actual size |
| Common Applications | Standard medical tools, small devices, consumables | Large instruments, combined sets, or packaging that requires size adaptability |
| Cost and Inventory | Pre-made pouches may be slightly more expensive per unit | Roll form reduces the need for multiple sizes, offering potential cost and inventory advantages |
| Ease of Operation | Simple to use, ideal for routine workflows | Requires higher coordination with sealing and cutting equipment |
In summary, compared with standard pouches, Gusseted Rolls provide greater flexibility and adaptability but require higher operational precision, proper sealing equipment, and trained personnel.
IV. How to Choose the Right Packaging for Different Scenarios?
Based on the above comparison and practical workflow in hospitals or laboratories, here are several recommended scenarios:
Scenario A: Daily Small Instrument or Consumable Packaging
Examples: Tweezers, scissors, probes, small consumables.
Recommended: Standard Sterilization Pouch
Reason: Instruments are of fixed size and quantity, processes are stable, and operation is simple. Short sealing time and high packing efficiency.
Scenario B: Combination Sets / Large or Irregular-Shaped Instruments
Examples: Surgical sets, folding tools, multi-component kits, large lab instruments.
Recommended: Gusseted Roll or Flat Roll
Reason: Customizable cutting length and gusset structure accommodate volume variation, reduce material waste, and improve adaptability.
Scenario C: High-Throughput Sterilization or Multi-Size Compatibility Needs
Examples: Central Sterile Supply Departments (CSSD) processing diverse instruments daily.
Recommended: Flat Roll or Gusseted Roll
Reason: A few roll sizes can meet multiple packaging needs, reducing inventory complexity and improving management efficiency.
Scenario D: Special Sterilization Methods or High-Risk Devices
Examples: Diagnostic instruments, endoscopes, or implant-related tools requiring strict sterility and packaging strength.
Recommended: High-quality Flat Roll or advanced-grade roll material.
Reason: Packaging failure risk is higher for these items; material and sealing quality must meet higher standards.
Selection should be based on a comprehensive assessment of instrument size and configuration, process frequency, inventory management needs, and sterilization method compatibility.
V. Why Is the Flat Roll Gaining More Attention in the Industry?
According to the Hopeway AMD industry analysis report "Why Sterilization Flat Roll Matters More Than You Think," several key advantages are noted:
Flat Rolls can be custom-cut to fit irregular or multi-component instruments, improving packaging efficiency.
They are compatible with multiple sterilization methods (steam, ethylene oxide, etc.), making them versatile in medical environments.
The transparent or semi-transparent film allows better visibility of contents, reducing packaging errors and improving operational safety.
Inventory management benefits from using roll material — fewer packaging SKUs are needed, reducing waste and simplifying storage.
From a broader industry perspective, as instrument diversity increases and sterile supply chain management becomes more complex and cost-sensitive, the advantages of Flat Rolls—efficiency, adaptability, and scalability—continue to grow in importance.
VI. Three Recommendations from Hopeway AMD for Packaging Decision-Makers
Based on the above analysis, Hopeway AMD suggests the following three priorities for professionals involved in packaging procurement and sterilization management:
1.Define Sterilization Methods and Instrument Types
Identify the sterilization process used (e.g., steam, EO, low-temperature gas) and the characteristics of the instruments being packaged (quantity, dimensions, and combinations). Using incompatible packaging materials poses significant risk.
2.Prioritize Materials and Seal Quality
When evaluating options, material selection should come first, followed by sealing reliability. Even the sealing technology cannot compensate for unsuitable material that degrades under sterilization conditions.
3.Choose Packaging Formats Flexibly Based on Actual Use
For stable and uniform instrument sizes: choose Standard Pouches.
For diverse or complex configurations: consider Flat Rolls or Gusseted Rolls.
For facilities managing numerous sizes or aiming to reduce waste: Roll-form packaging provides greater flexibility and efficiency.
VII. Industry Outlook
As global healthcare systems continue to raise standards for sterilization, safety management, and process efficiency, sterilization packaging technologies are also evolving.
The key future trends include:
Material innovation — development of higher-performance, biodegradable, and environmentally friendly materials.
Automation and validation — sealing equipment is becoming increasingly automated and capable of validation to minimize human error.
Greater flexibility in packaging design — to accommodate the growing diversity and combination of medical instruments and align with smart supply chain trends.
Multi-compatibility — more packaging products will be compatible with multiple sterilization methods, improving adaptability and cost efficiency.
Within this context, the Flat Roll format, known for its flexibility and efficiency, is expected to see continuous growth in both market share and professional attention.
In the field of medical sterilization packaging, a truly reliable material must balance three key dimensions: material performance, sealing integrity, and sterilization compatibility.
Meanwhile, the choice between standard sterilization pouches and gusseted rolls should be based on instrument specifications, combination complexity, workflow requirements, and inventory management considerations.
According to Hopeway AMD's analysis, Sterilization Flat Roll demonstrates distinct advantages across a wide range of applications. For procurement professionals, identifying and selecting packaging formats that align with their operational needs can significantly enhance sterilization safety, reduce operational costs, and improve process efficiency.
Looking ahead, as technology advances and industry demands evolve, sterilization packaging will become more adaptive, intelligent, and sustainable—and the role of the Flat Roll will become increasingly prominent in shaping the future of sterile packaging solutions.

 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Nederlands
Nederlands











 ‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
‘s-Gravenweg 542, 3065SG RotterdamThe Netherlands
 +31 (0)10 254 28 08
+31 (0)10 254 28 08







